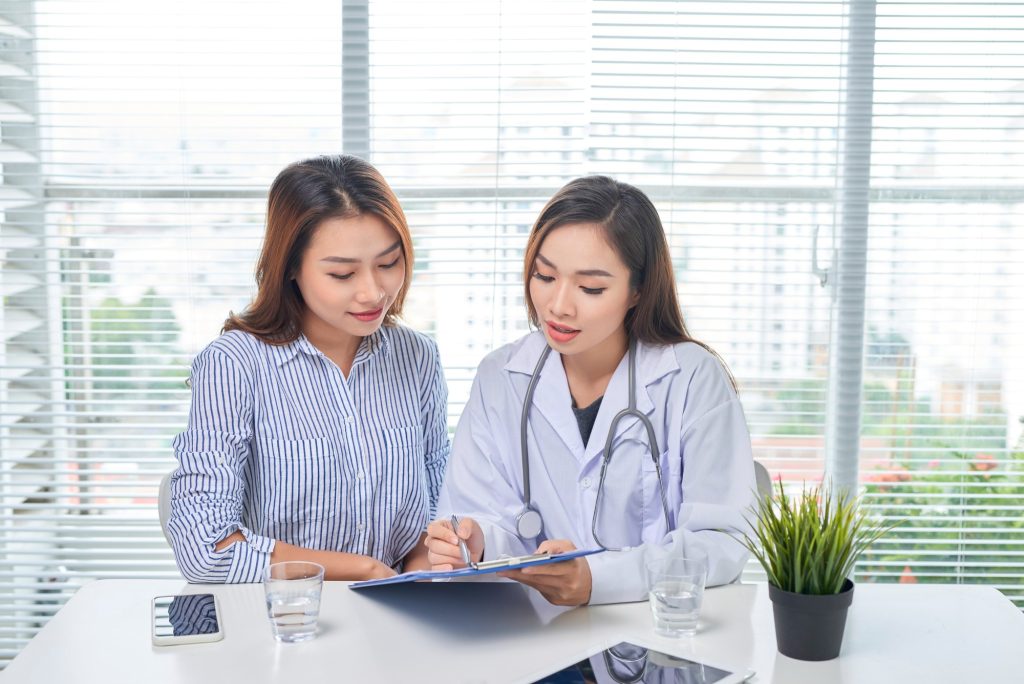
To customize treatment plans to individual needs, it is essential to discuss them with skilled healthcare professionals, as is the case with any medical intervention.
Scars resulting from injury, trauma, or surgical interventions are commonplace in medical practice. While some wounds undergo spontaneous regression, superficial and atrophic variants, such as rolling and boxcar scars, exhibit persistence, often leading to psychological distress in affected individuals. Thankfully, the evolution of medical technology has fostered the emergence of efficacious treatment modalities for such scars. Among these, soft tissue augmentation, also recognized as dermal fillers, stands out as a promising intervention. This article delves into soft tissue augmentation strategies’ mechanistic underpinnings and clinical efficacy in managing superficial and atrophic scars.
Comprehending Superficial and Atrophic Scars
Superficial scars predominantly afflict the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin. Manifesting flat lesions, they frequently stem from minor traumas or acne vulgaris. Conversely, atrophic scars denote a diminution of tissue, resulting in a depressed or concave contour. Rolling scars exhibit undulating features, whereas broader depressions with well-demarcated margins characterize boxcar scars. These varieties of scars exert a substantial impact on an individual’s psychosocial well-being and quality of life.
Soft Tissue Augmentation Techniques
Soft tissue augmentation entails the subcutaneous administration of dermal fillers to replenish volume and ameliorate scar appearance. Dermal fillers encompass diverse constituents, including hyaluronic acid, collagen, and synthetic polymers. These agents serve as scaffolds, elevating depressed regions of the skin and refining its texture.
Soft tissue augmentation’s pivotal advantage lies in its ability to stimulate collagen synthesis. Collagen, a structural protein pivotal for skin integrity, undergoes dwindling production with advancing age. By fostering collagen synthesis, dermal fillers enhance immediate scar aesthetics and engender enduring skin rejuvenation.
Diverse Dermal Fillers
Several dermal fillers are available, each endowed with unique properties and therapeutic indications. Hyaluronic acid fillers rank among the most utilized options for scar mitigation. Hyaluronic acid, an endogenous compound, facilitates skin hydration and elasticity. Hyaluronic acid fillers confer immediate volume augmentation upon injection into scars while catalyzing collagen biosynthesis.
Collagen-based fillers constitute another prevalent choice for soft tissue augmentation. Derived from bovine or human sources, these fillers provide transient enhancement in scar appearance. Although efficacious, the effects of collagen-based fillers are transient, necessitating periodic re-administration.
In recent years, synthetic fillers such as polylactic acid and calcium hydroxylapatite have garnered traction for scar management. These agents elicit gradual collagen induction, culminating in the protracted and sustainable enhancement of scar aesthetics. Additionally, synthetic fillers offer minimal allergic potential, given their non-animal derivation.
Treatment Protocol
The soft tissue augmentation procedure involves meticulously evaluating the scar and adjacent integument. In collaboration with the patient, healthcare practitioners ascertain the scar type, severity, and therapeutic objectives. Prior to the intervention, the skin is cleansed, and topical anaesthetics may be employed to mitigate procedural discomfort.
Dermal filler is meticulously introduced into scar locales using a fine-gauge needle. Injection techniques are tailored contingent on scar type and depth. After injection, a gentle massage may be performed to ensure uniform filler dispersion and mitigate irregularities.
Post-Procedural Care
Following soft tissue augmentation, patients are counselled to refrain from vigorous activities and sun exposure for a stipulated period. Transient oedema, erythema, or ecchymosis at injection sites is common but typically resolves expeditiously. Adherence to post-treatment directives promulgated by healthcare providers optimizes outcomes and curtails complications.
Outcomes and Long-Term Advantages
The aftermath of soft tissue augmentation for superficial and atrophic scars frequently manifests immediately after the procedure. As fillers integrate with perilesional tissues and spur collagen synthesis, scar appearance undergoes progressive amelioration in the ensuing weeks.
A salient merit of soft tissue augmentation resides in its enduring benefits. Unlike transient gains afforded by topical agents or laser interventions, dermal fillers engender sustained enhancement in scar aesthetics. With judicious maintenance and periodic touch-up sessions, patients can revel in smoother, more youthful cutaneous semblance over protracted durations.
Conclusion
Superficial and atrophic scars, exemplified by rolling and boxcar variants, greatly affect individuals’ psychological well-being. Soft tissue augmentation modalities, encompassing dermal fillers, offer a safe and efficacious avenue for scar amelioration. By reinstating volume, catalyzing collagen synthesis, and refining skin texture, dermal fillers empower individuals to reclaim confidence and esteem.
As with any medical intervention, consultation with proficient healthcare practitioners is imperative to tailor treatment strategies to individual needs. With the advent of advanced soft tissue augmentation techniques, individuals no longer endure the burden of unsightly scars but instead embrace the prospect of smoother, rejuvenated skin, fostering resolute self-assurance to confront the world.