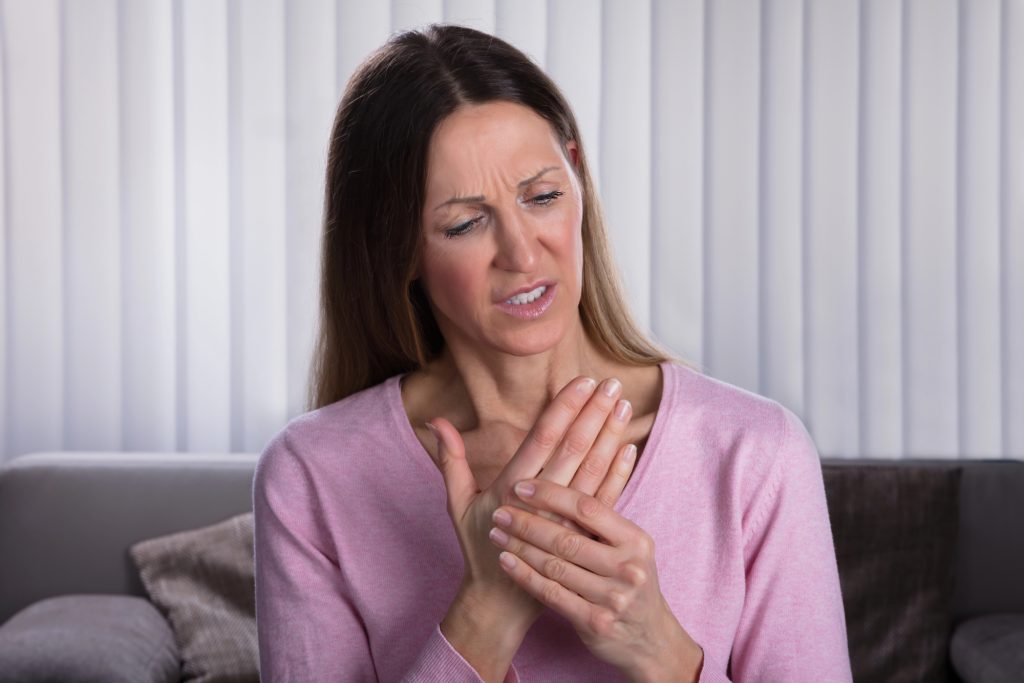
Botox, widely used to reduce wrinkles, is now being investigated for its ability to relieve pain linked to cancer, arthritis, and migraines.
Botox, a popular treatment for smoothing out wrinkles, is now being explored for its potential to alleviate the pain associated with cancer, arthritis, and migraines. This exciting development promises to offer significant pain relief without the side effects commonly seen with traditional pain medications.
Mechanism of Action
The primary component of Botox is botulinum toxin, which functions by inhibiting the transmission of nerve signals that cause muscle contractions. This inhibition prevents the formation of wrinkles. However, the same mechanism can be harnessed to block pain signals for extended periods.
Botulinum toxin works in tandem with tetanospasmin, a compound derived from the tetanus bacterium. When combined, these substances can deliver a potent analgesic effect by targeting the spinal cord and halting the transmission of pain signals to the brain. This innovative approach offers a new paradigm in pain management, potentially providing relief for months after a single injection.
Applications and Potential Beneficiaries
- Chronic Pain Conditions: Patients suffering from chronic migraines are among the prime candidates for this treatment. Chronic back pain sufferers and women experiencing post-cesarean section pain could also benefit significantly. Traditional painkillers often require multiple daily doses and provide only temporary relief, whereas a single injection of this new botulinum-based therapy could offer sustained pain relief for several months.
- Cancer Pain Management: Cancer patients endure severe pain, often managed with powerful opioids like morphine, which come with debilitating side effects. Botox injections could offer a safer alternative, reducing the reliance on opioids and improving the quality of life for cancer patients.
- Arthritis Relief: Arthritis patients experience constant joint pain, which significantly impacts their daily lives. Botox injections could potentially provide long-lasting pain relief, allowing patients to reduce or eliminate the need for daily pain medications and enjoy an improved quality of life.
Addressing Safety Concerns
One of the major hurdles in the widespread adoption of Botox for pain relief is the fear of paralysis in the treated area. To mitigate this concern, researchers have modified the botulinum molecule, attaching it to a non-toxic component of tetanospasmin. This modification ensures that the analgesic effects are delivered without causing paralysis, making the treatment both safe and effective.
The Future of Pain Management
The potential of Botox to revolutionize pain management is immense. Patients who are accustomed to multiple daily doses of painkillers could instead receive a single injection that provides months of relief. This not only simplifies the management of chronic pain but also reduces the risk of dependency on pain medications.
- Public Acceptance: The widespread use of Botox for cosmetic purposes suggests that the public is generally comfortable receiving injections for therapeutic reasons. This acceptance bodes well for the adoption of Botox-based pain treatments. Given that Botox is already approved for use in treating debilitating headaches, its application in broader pain management is a logical next step.
- Potential to Revolutionize Pain Treatment: The development of botulinum-based pain treatments represents a significant advancement in the field of pain management. By offering long-lasting relief without the side effects associated with traditional pain medications, Botox could become a cornerstone of chronic pain treatment.
Research and Development

Healthcare providers will require education on the updated uses of Botox and training in how to administer these treatments.
The ongoing research into the use of Botox for pain management is promising. Clinical trials are needed to further establish the safety and efficacy of this approach. If successful, these treatments could be integrated into standard pain management protocols, providing a new option for patients who suffer from chronic pain.
- Implications for Healthcare Providers: Healthcare providers will need to be educated on the new applications of Botox and trained in administering these treatments. As the adoption of botulinum-based pain management grows, it will be essential for medical professionals to stay informed about the latest research and techniques.
- Broader Impact on Pain Management Practices: The introduction of Botox for pain management could also lead to a broader re-evaluation of current pain management practices. As more effective and safer alternatives become available, the reliance on traditional pain medications, particularly opioids, may decrease, potentially reducing the incidence of opioid addiction and its associated societal impacts.
Conclusion
The potential of Botox to alleviate pain associated with chronic conditions like migraines, arthritis, and cancer without the side effects of traditional painkillers represents a major breakthrough in medical science. By modifying the botulinum molecule to avoid paralysis, researchers have paved the way for a new era of pain management. This innovation promises to improve the quality of life for millions of patients worldwide and could fundamentally change the way chronic pain is treated.
As research progresses and clinical trials validate the efficacy of these treatments, Botox could soon become a mainstay in pain management protocols. This advancement underscores the importance of continuing to explore and develop new therapeutic uses for existing medical treatments, expanding their benefits beyond their original applications.